Buying and planting tree seedlings for financial gain comes with an implied commitment. While the building you buy generates rental income next month, and the row crop you sow generates income within a year, the forest you plant returns cash periodically, with the first installment coming ten or more years in the future. It needs a little patience.
Opportunity Costs and the Time Value of Money
Investments always have an opportunity cost; once capital has been allocated, it is unavailable for other uses, such as buying a truck or fixing the deck. When planting trees, the dollars we “put in the ground” do not generate income for years, so we want a perspective on whether or not the decision could meet our financial objectives.
In practice, discounted cash flow (DCF) tools such as net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) address financial and valuation questions for investors, forest appraisers, and executives interested in timberland. Another approach to assess and communicate the financial implication of a forestry investment such as tree planting is to consider how $100 put in trees today must appreciate in order to cover the opportunity cost of this $100 applied elsewhere.
To assess the opportunity cost of $100 put in trees, we can compare its future value across a range of interest rates over time (see table). These rates can be hypothetical or represent actual alternative investments for our capital. For example, 30-year U.S. Treasury Bonds currently yield 2.91%. The dividend yields of publicly traded timberland-owning REITs range from 3.0% to 4.3% as of late-January 2018.
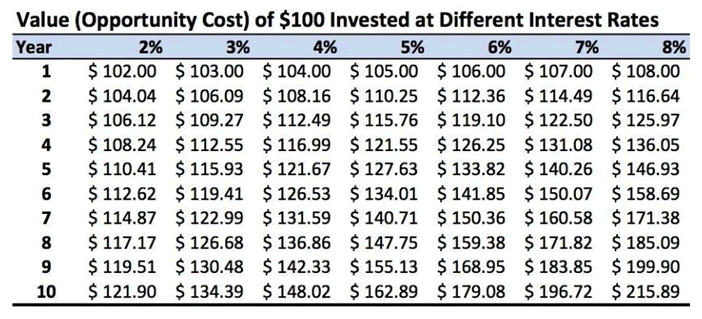
The table reinforces the power of compounded interest across rates and over time, and the impact and power of our investment decisions. The difference between a “certain” 3% return and a less certain 6% gain over ten years has material implications.
While I hear three primary reasons for owning or acquiring timberlands – to make money (investment), to manage risk (diversify a portfolio or secure wood supplies), and to recreate (huntin’ and fishin’), they all benefit from an understanding of opportunity cost. How else could we use our resources to meet our objectives? What else could we do with our time or money? And of our options, which should we choose? Basic financial tools and frameworks help organize our thinking to make optimal decisions given our opportunities and what we know at the time.
This content may not be used or reproduced in any manner whatsoever, in part or in whole, without written permission of LANDTHINK. Use of this content without permission is a violation of federal copyright law. The articles, posts, comments, opinions and information provided by LANDTHINK are for informational and research purposes only and DOES NOT substitute or coincide with the advice of an attorney, accountant, real estate broker or any other licensed real estate professional. LANDTHINK strongly advises visitors and readers to seek their own professional guidance and advice related to buying, investing in or selling real estate.










Add Comment